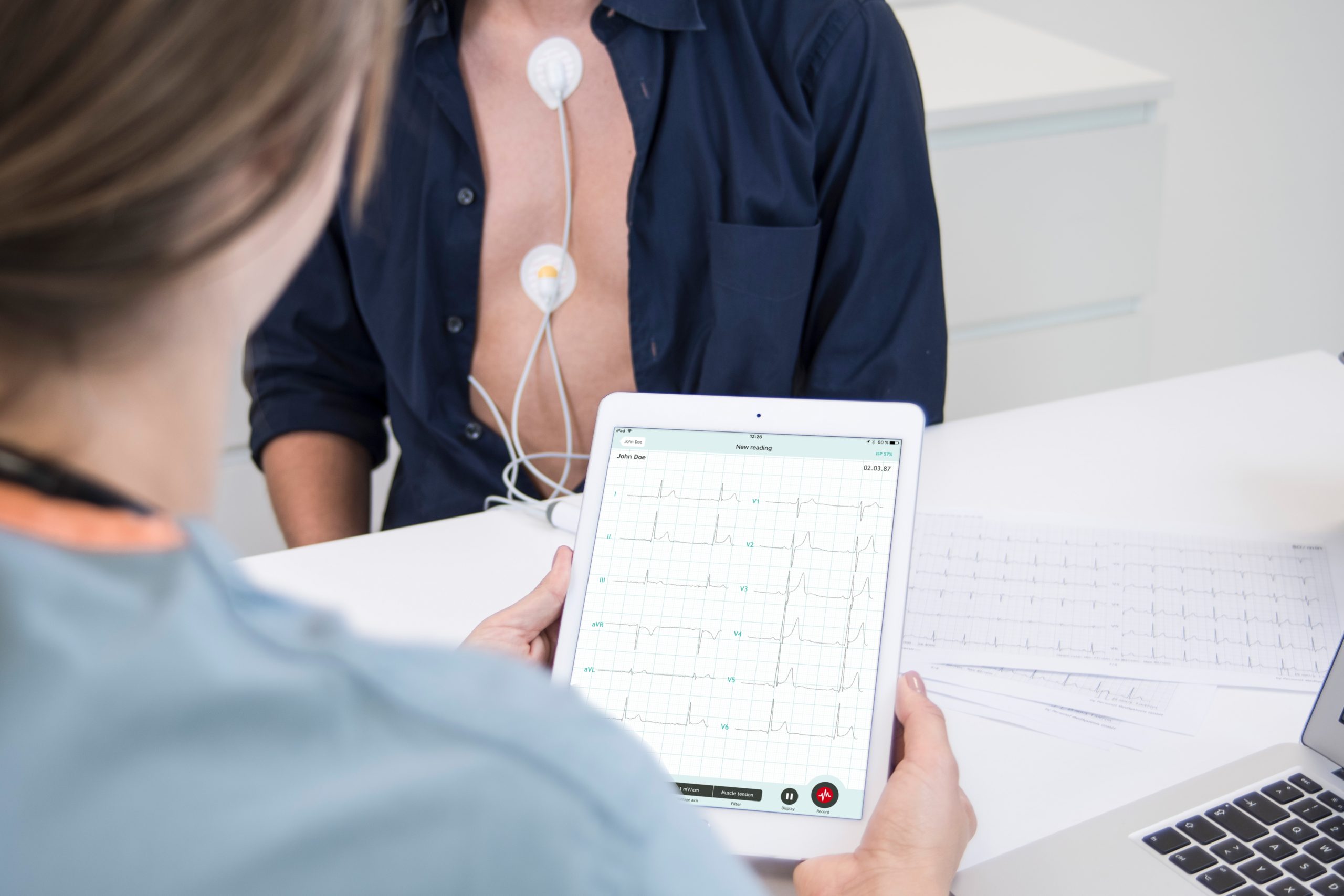
An electrocardiogram is one of the most important tests for your heart. If you’ve ever wondered what exactly this test shows, how it’s performed, and why it’s so critical for your health, this article will give you all the answers you need.
What Is an Electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram, also known as an ECG or EKG, is a medical test that records the electrical activity of your heart. Every time your heart beats, it generates an electrical signal that spreads through the cardiac muscle and causes it to contract. The electrocardiogram captures and displays these electrical signals in a graphical representation called an ECG tracing or curve.
The test is completely painless, non-invasive, and usually takes just a few minutes. However, it provides invaluable information about your heart health that can save lives.
Why Do You Need an Electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram is used to diagnose or monitor many cardiac conditions. Specifically, an ECG can detect problems such as arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), myocardial infarction, heart failure, problems with cardiac valves, and many other conditions that affect heart function.
Doctors recommend an electrocardiogram when you experience symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fatigue. It’s also used preventively in people with a family history of heart disease, in diabetics, in people with hypertension or high cholesterol, as well as before surgical procedures.
How Is an Electrocardiogram Performed?
The electrocardiogram procedure is simple and follows specific steps that ensure measurement accuracy.
Preparation for the Test
Before an electrocardiogram, no special preparation is required. It’s recommended not to apply lotion or cream to the chest skin on the day of the test, as this can affect electrode adhesion. Also, it’s good to inform your doctor about any medications you’re taking, as some may affect the results.
The Procedure Steps
During the test, you’ll be asked to lie down on an examination bed and remove clothing from the upper part of your body. The technologist or nurse will place small adhesive electrodes on your skin, usually on your chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes are connected with wires to a recording device called an electrocardiograph.
The placement of electrodes follows specific positions that have been internationally standardized to ensure accuracy. Typically, 10 electrodes are used that create 12 leads, which is why the test is often called a “12-lead ECG.” Each lead records the heart’s electrical activity from a different angle.
Once the electrodes are placed, you’ll be asked to remain still and breathe normally for a few seconds while the device records your heart’s electrical activity. The entire recording usually lasts 5-10 seconds, although the total duration of the test with preparation is approximately 5-10 minutes.
Special Types of Electrocardiograms
Beyond the standard resting ECG, there are other types of recordings:
- Stress ECG: Recorded while you exercise on a treadmill or exercise bike to assess how your heart functions under stress.
- Holter Monitoring (24-hour ECG): You wear a portable device for 24-48 hours that continuously records cardiac activity during your daily activities.
- Event Recorder: Similar to Holter, but only records when you activate it or when an abnormality is detected.
What Does an Electrocardiogram Show?
An electrocardiogram produces a characteristic curve with waves called P, Q, R, S, and T. Each wave represents a different phase of the cardiac cycle.
The P wave represents the excitation of the heart’s atria, the QRS complex shows the excitation of the ventricles, and the T wave represents ventricular recovery. Cardiologists analyze the shape, height, and duration of these waves, as well as the intervals between them, to detect any abnormalities.
A normal ECG tracing shows a normal heart rhythm (60-100 beats per minute in adults), normal electrical conduction, and absence of signs of damage or ischemia. However, an ECG can reveal problems such as bradycardia (slow heart rate), tachycardia (fast rate), atrial fibrillation, conduction blocks, signs of old or acute infarction, cardiac muscle hypertrophy, and other conditions.
Modern Solutions for ECG Recording
Technology has evolved significantly, and today there are portable devices that allow ECG recording outside the hospital.
Cardiosecur Pro: The Smart Choice for Professionals
The Cardiosecur Pro is a professional portable cardiograph that offers clinical-grade recording anywhere, anytime. This device allows for 22-lead ECG acquisition (more leads than the traditional 12-lead), providing an even more detailed picture of cardiac function.
Ideal for doctors, nurses, paramedical staff, and even for personal use under medical guidance, the Cardiosecur Pro connects to smartphones or tablets and provides immediate analysis of results. Its portability makes it perfect for home visits, sporting events, or emergency situations.
The device is medically certified and offers accuracy comparable to traditional hospital cardiographs, while being simple enough to use outside clinical settings.
Wellysis S-Patch ExL: Next-Generation Continuous Monitoring
For those who need long-term monitoring, the Wellysis S-Patch ExL Wearable ECG Patch is a revolutionary solution. This adhesive patch continuously records cardiac activity for up to 14 days without requiring recharging.
Unlike traditional Holter monitors that have wires and are bulky, the S-Patch ExL is discreet, waterproof, and doesn’t restrict your daily activities. You can shower, sleep, and continue your normal routine while the device records every heartbeat.
This advanced technology is ideal for detecting rare arrhythmias that may not appear during a short resting ECG. Data is transmitted wirelessly for analysis by specialist cardiologists who can detect even the most subtle cardiac abnormalities.
Who Should Have an Electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram is recommended for a wide range of people. Anyone experiencing symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, dizziness, or fainting should undergo an ECG as soon as possible.
Additionally, people with risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, family history of heart disease, or obesity should discuss regular ECG monitoring with their doctor. In many cases, an annual ECG can help with early detection of problems before they become serious.
Athletes, especially those participating in endurance sports, also benefit from regular ECG evaluation to ensure their heart can withstand intense physical stress. Many sudden cardiac arrests in young athletes could have been prevented with preventive screening.
Advantages of Electrocardiography
The electrocardiogram offers multiple advantages that make it an essential tool in modern medicine.
- First, it’s a completely safe and painless test with no side effects. There’s no radiation, and it can be repeated as many times as needed without risk to the patient.
- Second, it provides immediate results. In many cases, the doctor can see the results immediately after completing the test and proceed with diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Third, it’s an economical test compared to other imaging methods such as CT or MRI scans, but provides critical information about cardiac health.
- Finally, with modern portable technologies, access to ECG has become easier than ever, enabling timely detection and monitoring of cardiac conditions.
Limitations and Complementary Tests
Although the electrocardiogram is extremely useful, it has certain limitations. A normal ECG doesn’t always rule out the presence of heart disease, as some problems may only appear under specific conditions or at specific times.
For more comprehensive evaluation, your doctor may recommend complementary tests such as echocardiography (to see the heart’s structure and function), stress testing (to assess the heart under stress), Holter monitoring (for long-term surveillance), or coronary angiography (to view the heart’s blood vessels).
Conclusion
The electrocardiogram remains one of the most important and accessible tests for assessing cardiac health. Whether it’s a simple routine check or investigation of symptoms, an ECG provides invaluable information that can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment.
With modern technologies like the Cardiosecur Pro for professional use and the Wellysis S-Patch ExL for continuous monitoring, ECG recording has become more accessible, comfortable, and accurate than ever. Prevention and early detection of cardiac conditions are the key to a long and healthy life.
If you have questions about your cardiac health or wonder if you need an electrocardiogram, talk to your doctor. Your heart is precious and deserves the best possible care.
IMPORTANT DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
The information contained in this article is provided solely for informational and educational purposes. It does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical judgment.
Always consult your doctor or another qualified healthcare professional for any questions or concerns regarding your health. Do not discontinue, change, or start any treatment without your doctor’s advice. The information may not be complete or up to date for your personal situation.
In case of a medical emergency, call 166 immediately or go to the nearest hospital. The website and its authors are not responsible for any damages, losses, or complications arising from the use of this information. Each reader is responsible for their own health decisions.
Sources
- American Heart Association – Understanding Your ECG (www.heart.org)
- Mayo Clinic – Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) Overview (www.mayoclinic.org)
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute – Electrocardiogram Information (www.nhlbi.nih.gov)
- Cleveland Clinic – Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG) Guide (my.clevelandclinic.org)
- European Society of Cardiology – ECG Guidelines (www.escardio.org)
- Cardiosecur Pro Product Information – Avittia (www.avittia.com/el/product/foritos-kardiografos-cardiosecur-pro/)
- Wellysis S-Patch ExL Product Information – Avittia (www.avittia.com/el/product/s-patch-exl-wearable-ecg-patch/)
- Journal of Electrocardiology – Advances in Portable ECG Technology
- Circulation: American Heart Association Journal – ECG Screening Recommendations
- British Heart Foundation – Understanding Your Heart Tests (www.bhf.org.uk)